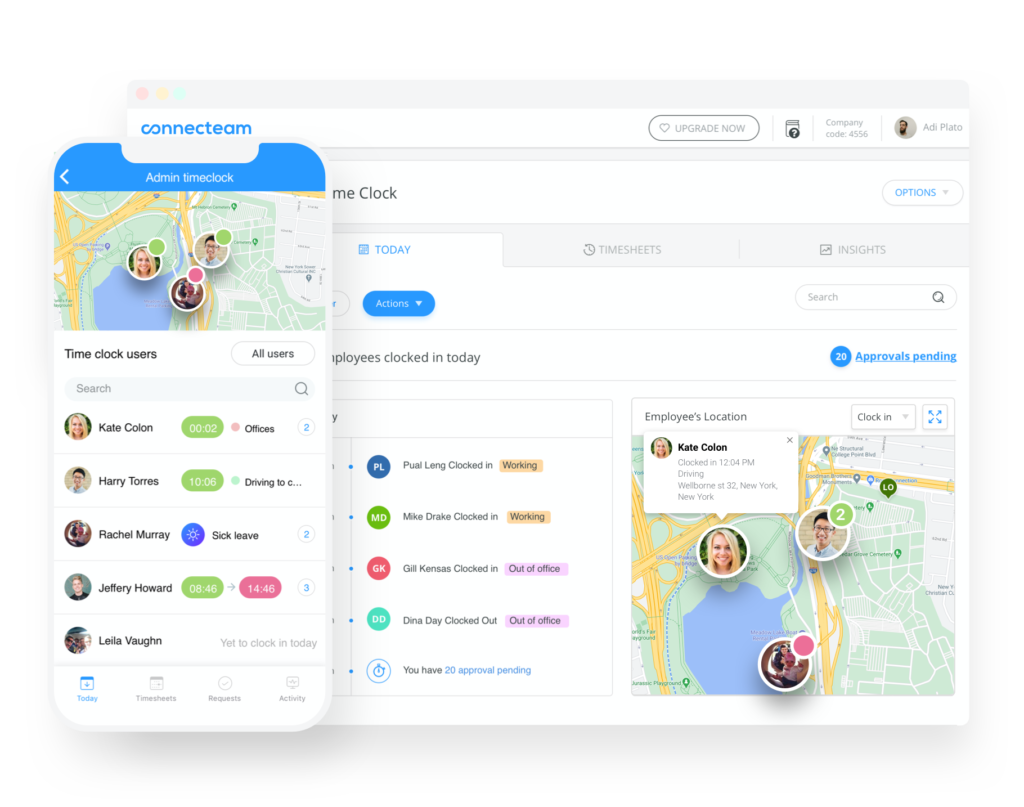
Knowing which pay period is best for your business can be confusing when you don’t have all the facts. We provide an in-depth guide on the most popular pay period options, what they each mean for your payroll, and what factors people often overlook.
Among the many decisions you’ll have to carefully consider as a business owner, figuring out which pay period best serves your company should take high priority. Although it may be tempting to just pick one and move on, there are many crucial factors to look at before you commit.
As a rule of thumb, you’ll want to make sure that employees are compensated enough for the sake of being fair, but also for the sake of productivity. To carefully do so, we go through the basics (what is a pay period) and other impactful factors that aren’t talked about enough.
Between salary and hourly wages, we have laid all of the options here in addition to extra information on how they operate and what it means for your payroll.
What Is a Pay Period?
The pay period definition is the time frame that employees are paid for the work completed. The exact time you decide to pay your employees is crucial as it determines the paycheck your employee receives. The pay period doesn’t usually change, and employees are therefore paid either on a weekly, biweekly, semimonthly, or monthly basis.
However, it’s important to check that you comply with the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) for the exact rules. In addition, any lunch breaks or vacation pay they may be entitled to. All employees’ salaries must be at least minimum wage or above. Here are the different payment options:
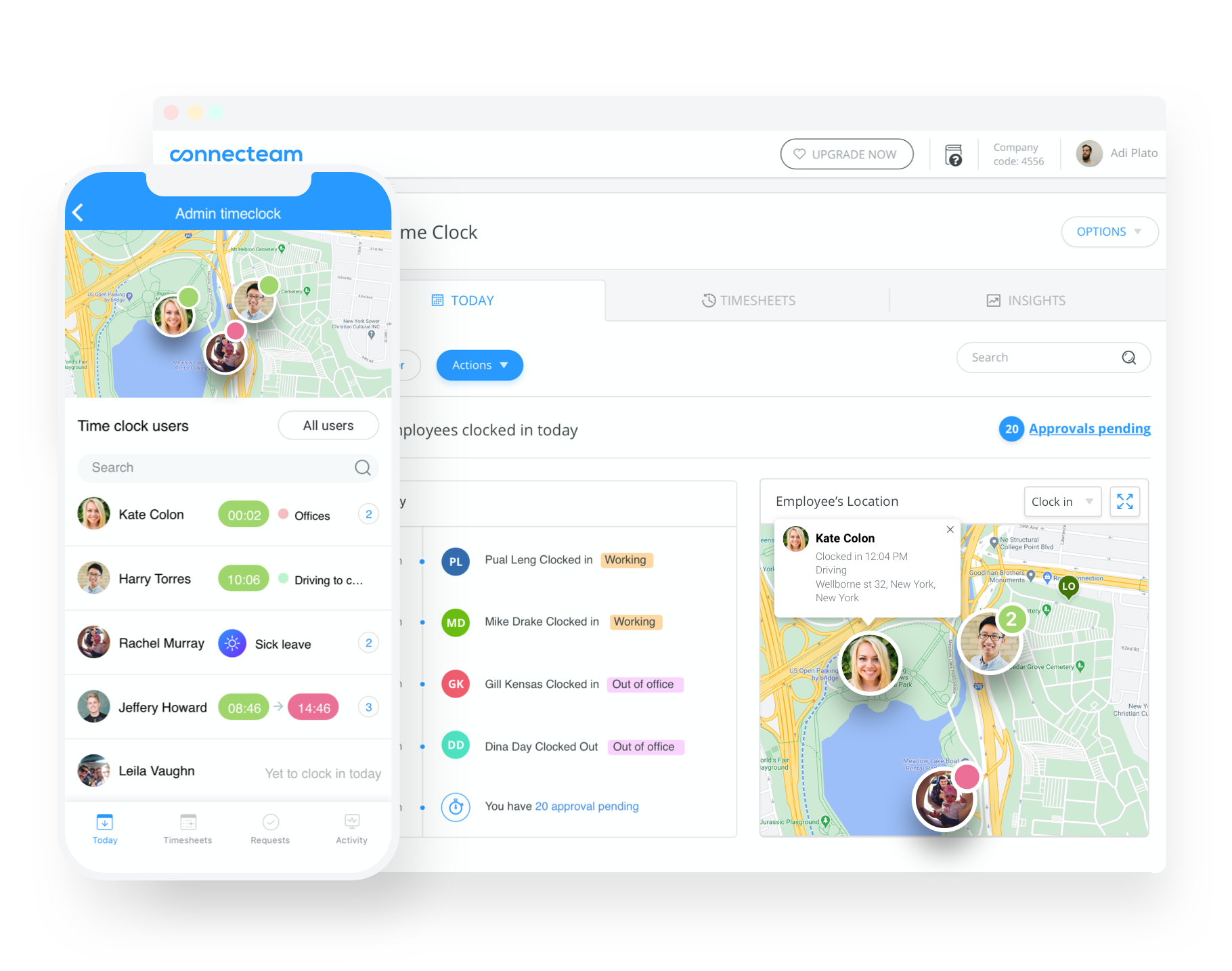
Simplify Your Payroll With Connecteam!
Track time with Connecteam and experience accurate payroll everytime! Say goodbye to time theft and buddy punching.
The 4 Common Pay Periods
Weekly:
You might ask, how many pay periods in a year? How many pay periods in 2021? A weekly pay period consists of 52 paychecks. Even though it’s called the weekly pay period, you choose the day of the week that it begins. This is very beneficial as a business because you can base it around when customers pay you. If your larger customers pay you on Friday, you can pay your staff on Saturday.
Weekly pay periods suit most businesses who pay their staff by the hour. Employees hand in their timesheets, including any overtime, to the payroll assistant, and it’s after being reviewed they receive their paycheck. Often payments can be in arrears, meaning workers hand in their timesheet and are paid a week later.
Pros to paying weekly:
- Employees who are living paycheck to paycheck can receive the money quicker to pay off outstanding bills
- Employees who have completed overtime know their money will be arriving soon
- Management has the ability to work out payroll easily because it’s only for a few days at a time
- Provides an incentive to work harder which could lead to increased productivity
- Employees benefit as they have constant cash flow
Cons to paying weekly:
- If you are outsourcing your payroll can be quite costly as you pay per transaction
- Often means you end up paying more as there are more paychecks per year
- Very time consuming and could create tax errors as it’s hard to maintain
Biweekly:
Another question on your mind is how many biweekly pay periods are there in a year? In addition, how many pay periods in 2021? A biweekly payroll consists of 26 pay periods or 27 in a year and occurs every other week.
Biweekly payments can be for both salaried and hourly employees. When employers ask themselves how many paychecks in a year? Biweekly could save time as payroll is twice a month. Biweekly payments can make taxes easier to process, and therefore fewer mistakes happen.
Pros to paying biweekly:
- Employees get paid more often
- Better than weekly paychecks as employees may not have time to cash them in on a weekly basis
- Cost-effective as you pay every other week. This is true especially if you use an outsource provider as you pay them only when needed
Cons to paying biweekly:
- This works out more expensive as employees receive more paychecks than semimonthly
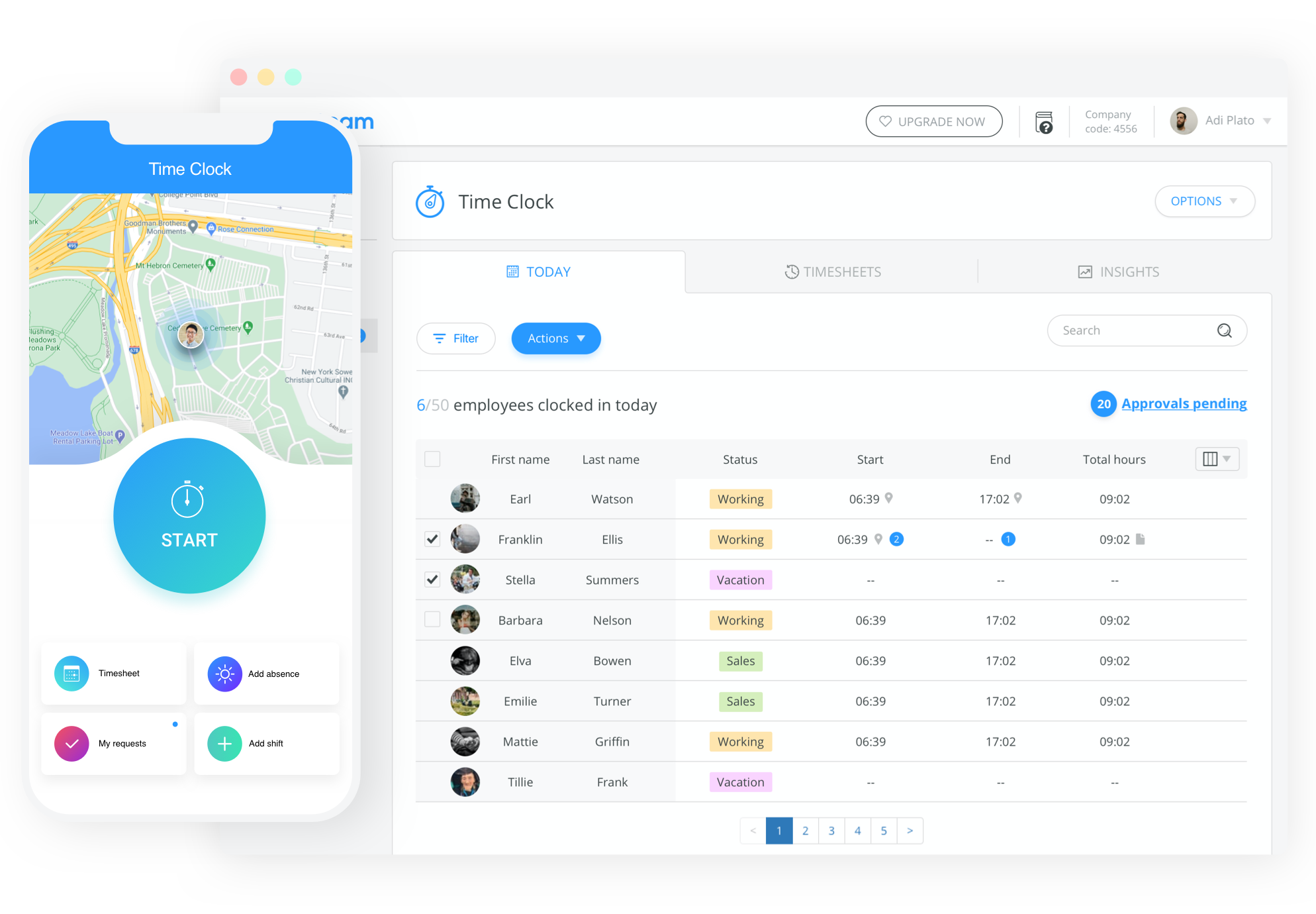
Connecteam – Accurate Payroll Everytime!
Schedule shifts, copy and paste previous weeks, approve sick days, vacation days, and so much more!
Semimonthly:
Your next question is so how many pay periods in a year? Semimonthly is twice a month always on the same date. This type of payment is usually for the salaried worker. How many paychecks in a year? They are given 24 paychecks over the year.
Pros of semimonthly payments:
- Employees know the exact dates they are expected to be paid.
- Helps you manage your cash flow
Cons of semimonthly payments:
- Payroll workers need to be sure they have counted all the days correctly as even though they are on the same date each month, the amount of time passed from the previous salary may be different
- Difficult for hourly employees if they have completed overtime, they have to submit by a certain date or they have to wait until the next paycheck
- New employees might have to wait for the first salary
Monthly:
If you’re wondering how many paychecks in a year for monthly salaries? Monthly pay periods are very common for salaried employees. How many paychecks in a year? The worker receives 12 payments throughout the year.
Pros of monthly payments:
- Great for invoicing employees as they receive monthly payments
- This is the least amount of work as payroll is calculated once a month
Cons of monthly payments:
- Employees are not always happy with this arrangement as they have to wait to be paid
- New employees have to wait for the first paycheck
7 Things to Consider When Choosing Pay Periods
-
Gross Pay
-
Leap years
-
Accuracy in attendance tracking & payroll
-
Employee Labor Rights
-
Cash Flow
-
Employee Benefits
-
Employee Labor Laws (Federal & State)
Gross pay is often confused with net pay. Gross pay is the total amount that is owed to each employee before mandatory (federal taxes) and voluntary (insurance and retirement) deductions have kicked in. The total amount after deductions is called net pay.
Net pay is the number employees care about most because it’s the real total that’ll be put into their bank account. However, on your end, the most important for you to focus on is the gross pay because deduction amounts (from gross pay) will fluctuate based on your pay period frequency.
When a day is added to keep up with the Earth’s natural rotation, this is what is called a Leap Year. You might be wondering what astronomy has to do with pay periods? Well if you go by a weekly or bi weekly pay period, this additional day will result in an overpayment. This is something you can only prepare yourself for and accommodate accordingly.
When you’re paying your employees on an hourly wage, every hour, minute, and second counts towards your end payroll. This can be tiresome to keep track of but in order to avoid overpaying or underpaying it’s your responsibility to maintain accuracy.
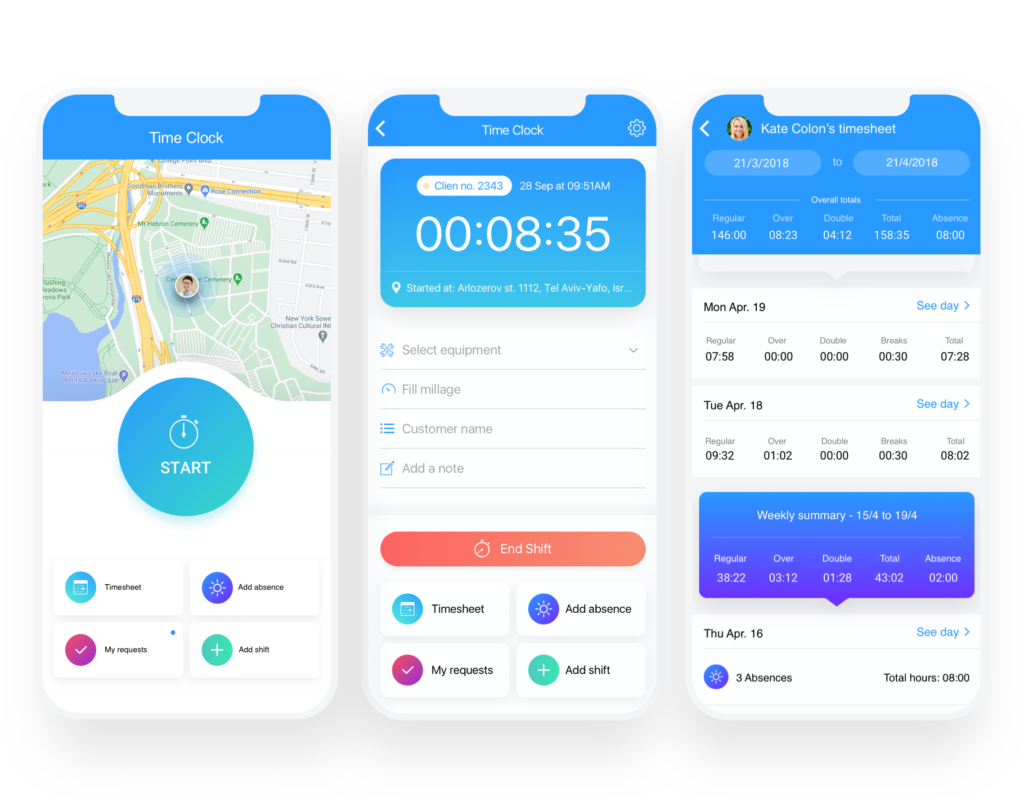
The best way to do so is to implement an automated time clock that will mark attendance (clock in’s, out’s, breaks, & overtime) for you. A software system like this is often coupled with a payroll software or service that’ll make everything from attendance to payroll absolutely seamless.
Depending on what pay period you choose, services like these can keep your finances timely and accurate.
Employees have more control over pay periods than you may think. Some state labor laws hand over the rights to employees to decide which pay period works best for them. If you know this is true for your state, talk with your employees and see if you can find a happy middle ground.
Know that the more frequent your pay periods are, the more payroll will cost you. So if you can figure out what will make both you and your employees happy, that would be best!
Depending on your industry and the make-up of your business, cash flow will differ. Knowing when cash flow will reach its peaks and lows is super important to prepare for. A lot of problems would arise if you couldn’t pay your employees in time, due to a lack of cash flow.
This being said, do some research and calculations to predict what your cash flow will be, and go from there.
Employee benefits are a perk for you just as much as they are for your employees. Offering options such as life insurance and pension better the lives of your employees, but it also makes employees more inclined to want to work for you.
Although this is a massive plus, employee benefits can come at a cost. However, depending on the pay period you choose, you might be able to make certain employee benefits are tax deductible. Finding which pay period supports a more cost-effective route for you without cutting benefits short should be your goal.
At the end of the day, you’ll want to comply with the law. When you go to pick your pay period, make sure it complies with both state and federal laws. Federal labor laws are dictated by the Fair Labor Standards Act, which includes minimum wage and overtime. This is extremely important to follow and stay on top of. In addition to this, state labor laws will set rules and regulations specific to the industry in which you categorize as.
When it comes to the time of actually counting overtime and break time, use an employee management software system that can automatically record employee work hours for you!
Choosing the Best Pay Period for Businesses
When choosing the correct pay period for your business, there are a few factors to consider.
First, you’ll need to estimate how many people you plan on employing. The next step is pretty straight forward as well. Pick whether an hourly wage or giving a set salary is better. If you opt for hourly work, a weekly or bi-weekly payroll might be best for you. Whereas when hiring salaried employees, a semi-monthly or monthly salary would be a better fit.
When making this decision it would be wise to put your employees first, as this increases the likelihood of them staying longer and could dramatically increase morale. This means you should also put thought into what type of employee you’re looking to hire. If the employee can’t afford going from paycheck to paycheck, then opting for a weekly or bi-weekly pay period is a good option.
Cash flow is another key influencer on the pay period you choose. If you’re a small business, think about how often money is coming into the business. If you have standing orders, be sure to know the dates that those customers will be paying. Once you know the dates and amounts, you can figure out which pay period is most suitable for both you and your staff.
Certain states may have set rules for your business and/or industry. So before you set anything in stone, it’s best to check with your accountant to ensure the pay period you’ve picked complies with the laws that apply to you.
The Bottom Line On Setting A Pay Period
Once you’ve decided on the payroll system that suits your business, you are ready to go. Remember that payment is a crucial part of any job, and even if your employee loves what they do, everyone likes to receive money. Paying your employees on time and according to the law is what will create a happy working environment.
Connecteam – Leading Time Tracking App
Easily track and manage work hours on jobs and projects. Improve your payroll process and the way you manage timesheets like never before. Set up in as little as 15 minutes!