The HIPAA privacy rule plays a vital role in protecting the privacy and security of individuals’ health information. Learn everything you need to know below.
Key Takeaways
- The HIPAA Privacy Rule is a federal regulation that governs the use and disclosure of protected health information (PHI).
- It was proposed in 1999 and finalized in 2000. It wasn’t until 2003 that covered entities were required to be in compliance
- The rule applies to covered entities, including healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses.
- Its purpose is to protect the privacy and security of individuals’ health information and give patients control over their own health data.
- Compliance with the HIPAA Privacy Rule is essential for covered entities to maintain patient trust and avoid penalties for non-compliance.
Quick HIPAA Privacy Rule History
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was enacted in 1996 to address various healthcare issues, including health insurance portability and fraud prevention.
In 1999, the HIPAA Privacy Rule was proposed to establish standards for protecting individuals’ health information. After a year of deliberation, the Privacy Rule was finalized in 2000, outlining the requirements and guidelines that covered entities must follow to ensure the privacy and security of patient data.
By 2003, covered entities were required to be in compliance with the HIPAA Privacy Rule, including implementing necessary safeguards and administrative measures to protect patients’ health information. Since then, enforcement and penalties have been in place to hold violators accountable for their actions.
In 2009, the HITECH Act was introduced to strengthen certain aspects of HIPAA, focusing on the security and privacy of electronic health records (EHR) and promoting technology adoption in healthcare.
In 2013, the Omnibus Rule was implemented to update and clarify the provisions of the HIPAA Privacy Rule.
Since the Omnibus Rule, there have been subsequent developments to address emerging issues in healthcare data privacy and security as technology advances and new challenges arise in protecting patient information.
Did You Know?
HIPAA’s Privacy Rule was an evolutionary step in medical privacy, paving the way for digital health records and enhancing patient trust in the digital age.
Why Does the HIPAA Privacy Rule Exist?
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Privacy Rule exists primarily to protect the privacy and confidentiality of individuals’ protected health information (PHI).
Here are some key reasons why the HIPAA Privacy Rule was established:
- Patient privacy: The rule aims to safeguard patients’ privacy rights by regulating how covered entities (healthcare providers, health plans, healthcare clearinghouses) handle and disclose personal health information.
- Prevent misuse of health data: It prevents the unauthorized or inappropriate use and disclosure of sensitive health information that could potentially result in discrimination, stigmatization, or embarrassment for individuals.
- Improve healthcare provider practices: The rule sets national standards for the protection of health data, promoting better privacy practices among healthcare organizations and their business associates.
- Increase trust in the healthcare system: By ensuring the confidentiality of personal health information, the HIPAA Privacy Rule aims to build trust between patients and healthcare providers, encouraging individuals to seek medical treatment without fear of their information being misused.
- Facilitate secure information sharing: The rule establishes guidelines for the secure transmission and sharing of health data among authorized entities, enabling better care coordination while maintaining privacy protections.
- Address technological advancements: As healthcare increasingly relies on electronic health records and digital data exchange, the HIPAA Privacy Rule provides a framework for protecting sensitive information in the digital age.
The HIPAA Privacy Rule balances protecting individuals’ privacy rights regarding their health information and enabling the appropriate use and disclosure of such information for medical treatment, payment, and healthcare operations.
What Businesses Must Comply with the HIPAA Privacy Rule?
The HIPAA Privacy Rule applies to various entities involved in healthcare, including:
- Healthcare Providers: This category includes doctors, clinics, hospitals, psychologists, dentists, nursing homes, and other professionals and institutions that provide medical services.
- Health Plans: Health insurance companies, health maintenance organizations (HMOs), government health programs like Medicaid and Medicare, and employer-sponsored health plans fall under the category of health plans.
- Healthcare Clearinghouses: These entities process health information received from another entity into a standardized format, making it easier to exchange and share.
In addition to these covered entities, the HIPAA Privacy Rule also extends its requirements to business associates.
Business associates are individuals or entities that provide services to covered entities and handle PHI on their behalf. These may include billing services, consultants, and IT service providers.
All these entities must comply with the HIPAA Privacy Rule to ensure the privacy and security of individuals’ health information.
Pro Tip
Regularly update your team and systems to stay compliant with HIPAA. Utilizing a HIPAA-compliant healthcare management platform like Connecteam can simplify this process, ensuring everyone is up-to-date with the latest privacy standards.
Get started with Connecteam for free today!
What Happens When You Violate HIPAA Regulations?
Violating HIPAA regulations can result in significant consequences for individuals and organizations involved. The Office for Civil Rights (OCR), a US Department of Health and Human Services division, is responsible for enforcing the HIPAA Privacy Rule and ensuring compliance with its provisions.
When a HIPAA violation occurs, penalties can be imposed based on the severity of the violation. The fines for HIPAA violations can range from $100 to $50,000 per violation, depending on various factors such as the nature and extent of the violation, the harm caused, and the level of negligence involved.
In addition to financial penalties, individuals or organizations that knowingly violate HIPAA regulations may face civil or criminal liability. Civil liability can result in legal action brought by affected individuals seeking compensation for damages caused by the violation. Criminal liability may lead to criminal charges, prosecution, and potential imprisonment.
It is crucial to note that HIPAA violations not only compromise patient privacy and rights but also undermine trust in healthcare providers and organizations. Maintaining the confidentiality of protected health information and respecting patient rights are fundamental to upholding the principles of ethical healthcare.
By adhering to the HIPAA Privacy Rule, healthcare professionals can protect patient information, maintain legal compliance, and foster patient trust and confidence.
Complying with HIPAA regulations is a legal obligation and an ethical responsibility to safeguard patient privacy and uphold the rights of individuals receiving care.
Pro Tip
Perform regular risk assessments to identify potential violations of HIPAA regulations before they occur. A proactive approach can save your organization from hefty penalties.
Who Falls Under the HIPAA Privacy Rule?
The HIPAA Privacy Rule applies to various entities and individuals involved in healthcare and the handling of PHI.
Covered entities, including health care providers, health plans, and health care clearinghouses, are directly subject to the Privacy Rule’s requirements.
Healthcare providers encompass doctors, hospitals, clinics, pharmacies, and other professionals and institutions providing medical services.
Health plans include insurance companies, employer-sponsored plans, and government health programs.
Healthcare clearinghouses are responsible for processing health information in a standard format.
In addition to covered entities, the Privacy Rule also extends to business associates, such as billing services or consultants, who handle PHI on behalf of covered entities.
Did You Know?
While HIPAA sets the floor for privacy standards, states can enact stricter laws to protect health information. This layered approach means that compliance can vary significantly from one state to another, making it crucial for healthcare entities to understand both federal and state regulations.
How Does the Rule Protect Individuals’ Rights?
The HIPAA Privacy Rule is designed to safeguard and protect individuals’ rights when it comes to their health information.
It provides essential measures to ensure privacy, control, and authorization over personal health data.
Here are some key aspects of how the rule protects individuals:
- Right to Access Health Information: Individuals have the right to access and request copies of their health records maintained by covered entities. This allows individuals to stay informed and take an active role in managing their health.
- Control Over Health Data: The HIPAA Privacy Rule gives individuals control over the use and disclosure of their PHI for most purposes. Individuals have the power to authorize or deny sharing their health information, which helps protect their privacy and confidentiality.
- Authorization Requirements: While individuals have control over their health data, the Privacy Rule does outline exceptions to the authorization requirement. These exceptions include reporting diseases, birth and death information, and injury cases. This balance ensures appropriate information sharing for public health and safety purposes.
- Patient Consent: Patient consent plays a crucial role in the protection of health information. The Privacy Rule requires covered entities to obtain the individual’s consent before making certain uses and disclosures of PHI. This consent ensures that individuals have a say in how their health information is used and shared.
- Guidance from the US Department of Health and Human Services: The US Department of Health and Human Services provides valuable guidance and resources to help individuals understand their rights under the HIPAA Privacy Rule. This helps individuals navigate the complex landscape of health information privacy and make informed decisions.
What Information Is Protected?
The HIPAA Privacy Rule provides comprehensive protection for individuals’ health information.
It covers an individual’s past, present, and future physical or mental health conditions, as well as their medical history.
This includes information related to an individual’s physical or mental health, such as medical diagnoses, treatments, medications, and medical test results.
The Privacy Rule also covers healthcare transactions and payments.
This includes information related to providing health care to the individual, such as medical procedures, hospital visits, and laboratory tests.
It also includes health care payments, such as health insurance claims and billing information.
Under the HIPAA Privacy Rule, health records and other identifiable health information held or transmitted by covered entities are considered protected health information.
Covered entities, including health care providers, health plans, and health care clearinghouses, must comply with the Privacy Rule’s regulations to ensure the privacy and security of individuals’ health information.
Covered Entities
Covered entities, including healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses, play a crucial role in maintaining the privacy and security of patients’ health information.
To ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations, covered entities have specific responsibilities outlined in the HIPAA Privacy Rule.
1. Protecting Patient Confidentiality: Covered entities are obligated to safeguard the confidentiality of patients’ health information. This includes implementing appropriate administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to prevent unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of protected health information.
2. Obtaining Necessary Authorizations: Before disclosing PHI, covered entities must obtain the necessary patient authorizations. This ensures that patients have control over their health information and can make informed decisions regarding its use and disclosure.
3. Implementing Security Measures: Covered entities must implement and maintain robust security measures to protect health information from unauthorized access or disclosure. This involves employing encryption, secure data storage, access controls, and regular system monitoring to identify and address any potential security vulnerabilities.
4. Compliance with HIPAA Regulations: Covered entities must have policies and procedures in place to ensure compliance with all aspects of the HIPAA Privacy Rule. This includes training employees on HIPAA regulations, conducting regular risk assessments, and promptly addressing any breaches or violations that may occur.
5. Preventing Penalties for Non-Compliance: Compliance with HIPAA regulations is essential for covered entities to avoid penalties for non-compliance. Failure to adhere to the Privacy Rule can result in substantial fines, legal action, and damage to the reputation and trust of the healthcare provider or organization.
By fulfilling their responsibilities under the HIPAA Privacy Rule, covered entities play a vital role in protecting patient privacy and maintaining the integrity of the health care system.
Compliance with HIPAA regulations ensures that patients’ health information remains confidential and secure, fostering trust between healthcare providers and patients.
This Might Interest You
Stay compliant and safeguard sensitive information! Read our in-depth review of the best HIPAA compliance software to ensure your business meets regulatory standards and avoids costly penalties. Plus, explore the best HIPAA-compliant texting apps to securely communicate with your team and clients. Find the right tools to protect your business today!
Permitted Use and Disclosure of PHI
The HIPAA Privacy Rule establishes clear standards for using and disclosing Protected Health Information by covered entities.
Covered entities can use and disclose PHI without patient consent for authorized purposes, which include treatment, payment, and healthcare operations.
This allows healthcare providers to effectively provide care, process payments, and conduct necessary operations.
However, for most other uses and disclosures of PHI, patient consent is generally required.
In addition to authorized purposes and patient consent, the HIPAA Privacy Rule also permits the use and disclosure of PHI for specific purposes, such as public health activities and law enforcement purposes.
These uses, and disclosures are subject to certain criteria and safeguards to balance the need for information sharing with patient privacy and data security.
Effortlessly Maintain HIPAA Compliance with Connecteam
Fortunately, there are technology solutions on the market that can help you remain HIPAA compliant and avoid violations.
Connecteam is an industry-leading employee management platform designed to make communication, scheduling, task management, training, and payroll a whole lot easier. What’s more, the app is HIPAA-compliant so you don’t have to worry about data breaches or violations while using the app.
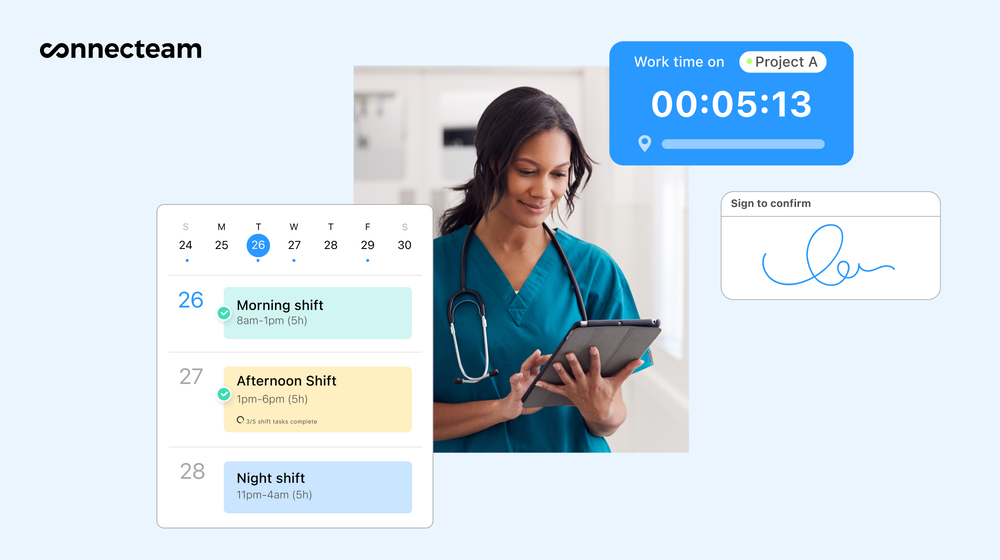
So whether you work for a healthcare organization or contract with one regularly, here’s how Connecteam can help your business remain HIPAA-compliant:
Create your own customized HIPAA training courses for your staff
Ongoing training is a crucial component of preventing HIPAA violations. And according to industry standards, you should provide refresher courses for your staff annually.
With Connecteam’s employee training software, you can create customized training courses directly in the app and make them as detailed as you like. Mix up the training materials and keep employees engaged by adding images, videos, gamification elements, and quizzes to test their knowledge.
Employees can complete courses on their own time from their mobile devices to avoid expensive and timely in-person training sessions.
Protect employee and patient data with 2FA, SSO, and data encryption
Connecteam offers cloud-based document storage where employees can submit certifications, employment documents, and other files in seconds. You can also share patient documents, scans, or any other PHI within the app for streamlined information sharing without worrying about a HIPAA breach.
Connecteam helps you secure employee and patient data with 2-factor authentication (2FA), single sign-on (SSO), and data encryption. You can also set up a password policy requiring employees to use strong passwords for their Connecteam accounts.
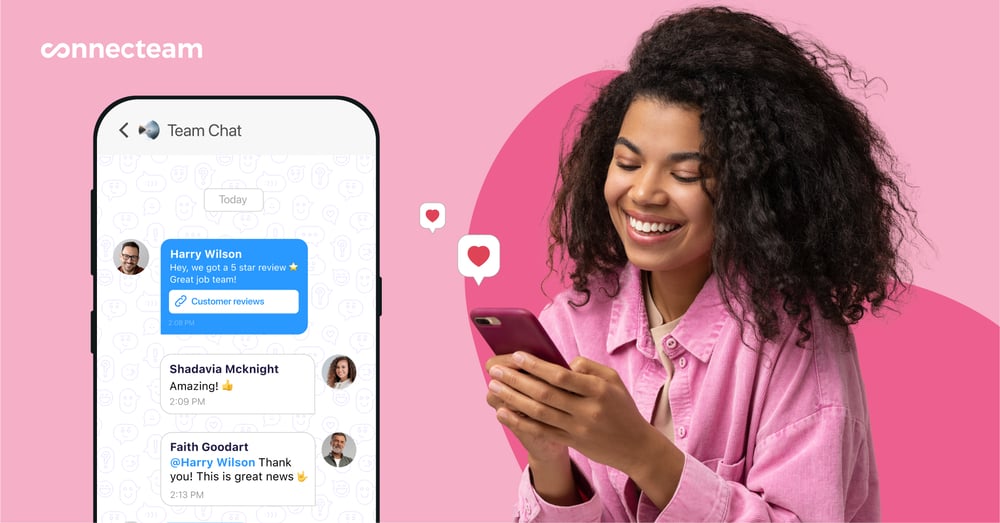
Communicate and share data with 1:1 and group messaging
With the user-friendly, fully HIPAA-compliant employee chat app, you can create an unlimited number of individual and group chats and share images, videos, documents, and other files directly through messages.
All chat data is end-to-end encrypted, and you can also set customized user access permissions to ensure that only authorized users can access certain conversations.
For extra security, conversations are saved to the cloud and not on users’ devices. This also prevents staff from downloading or exporting chat data.
Set up user access permissions and monitor data use with audit logs
Connecteam makes it easy to assign role-based access permissions to control who has access to what data. This is crucial for maintaining HIPAA compliance since it ensures that only employees who need access to sensitive health information have it.
You can also create custom groups to control permissions or set permissions individually. Connecteam lets you control who can access different chat channels, documents, and forms.
Connecteam is designed for healthcare organizations of any size
Connecteam isn’t just user-friendly and customizable: it’s also affordable. Basic pricing plans start at only $29/month, and small businesses with under 10 users can use the app’s basic features completely for free.
Note: These prices do not reflect the additional fee of adding HIPAA compliance to an account.
Stay compliant with HIPAA and Prevent Violations
HIPAA violations not only compromise patient privacy but also can result in significant legal and financial repercussions. It’s crucial for healthcare professionals and organizations to strictly adhere to HIPAA regulations to ensure the confidentiality and security of private patient information.
With a HIPAA-compliant employee management app like Connecteam, you can provide regular HIPAA refresher trainings, secure employee communication, and ensure your data is encrypted, reducing the risk of a violation.




